Exxon Counterattacks California’s Climate Disclosure Laws

Current conditions: Hurricane Melissa exploded in intensity over the warm Caribbean waters and has now strengthened into a major storm, potentially slamming into Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti, and Jamaica as a Category 5 in the coming days • The Northeast is bracing for a potential nor’easter, which will be followed by a plunge in temperatures of as much as 15 degrees Fahrenheit lower than average • The northern Australian town of Julia Creek saw temperatures soar as high as 106 degrees.
THE TOP FIVE
1. Exxon sued California
Exxon Mobil filed a lawsuit against California late Friday on the grounds that two landmark new climate laws violate the oil giant’s free speech rights,The New York Times reported. The two laws would require thousands of large companies doing business in the state to calculate and report the greenhouse gas pollution created by the use of their products, so-called Scope 3 emissions. “The statutes compel Exxon Mobil to trumpet California’s preferred message even though Exxon Mobil believes the speech is misleading and misguided,” Exxon complained through its lawyers. California Governor Gavin Newsom’s office said the statutes “have already been upheld in court and we continue to have confidence in them.” He condemned the lawsuit, calling it “truly shocking that one of the biggest polluters on the planet would be opposed to transparency.”
2. China may delay its rare earth export controls
China will delay introducing export controls on rare earths, an unnamed U.S. official told the Financial Times following two days of talks in Malaysia. For years, Beijing has been ratcheting up trade restrictions on the global supply of metals its industry dominates. But this month, China slapped the harshest controls yet on rare earths. In response, stocks in rare earth mining and refining companies soared. Despite what Heatmap’s Matthew Zeitlin called the “paradox of Trump’s critical mineral crusade” to mine even as he reduced demand from electric vehicle factories, “everybody wants to invest in critical minerals startups,” Heatmap’s Katie Brigham wrote. That — as frequent readers of this newsletter will recall — includes the federal government, which under the Trump administration has been taking equity stakes in major projects as part of deals for federal funding.
3. Bill Gates’ nuclear company gets approval for environmental plan
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission rewarded Bill Gates’ next-generation reactor company, TerraPower, with its final environment impact statement last week. The next step in the construction permit process is a final safety evaluation that the company expects to receive by the end of this year. If everything goes according to plan, TerraPower could end up winning the race to build the nation’s first commercial reactor to use a coolant other than water, and do so at a former coal-fired plant in the country’s top coal-producing state. “The Natrium plant in Wyoming, Kemmerer Unit 1, is now the first advanced reactor technology to successfully complete an environmental impact statement for the NRC, bringing us another step closer to delivering America’s next nuclear power plant,” said TerraPower president and CEO Chris Levesque.
4. Judge orders New York to come out with cap-and-invest program rules
A judge gave New York Governor Kathy Hochul’s administration until February 6 to issue rules for its long-delayed cap-and-invest program, the Albany Times-Union reported. The government was supposed to issue the guidelines that would launch the program as early as 2024, but continuously pushed back the release. “Early outlines of New York’s cap and invest program indicate that regulators were considering a relatively low price ceiling on pollution, making it easier for companies to buy their way out of compliance with the cap,” Heatmap’s Emily Pontecorvo wrote in January.
5. Wind, solar, and batteries are supplying increased demand in Texas
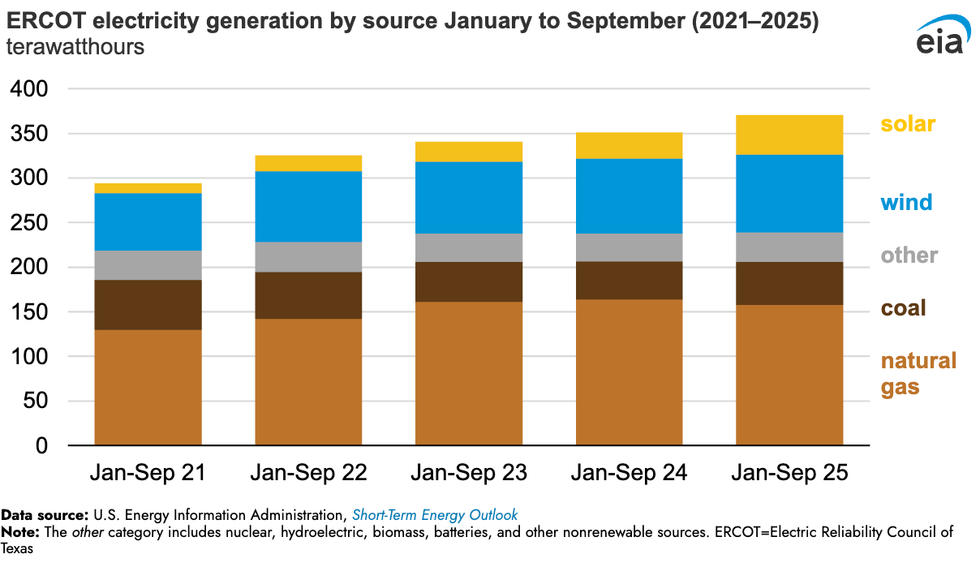
The Texas data center boom is being powered primarily with new wind, solar, and batteries, according to new analysis by the Energy Information Administration. Since 2021, electricity demand on the independent statewide grid operated by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas has soared. Over the past year, wind, solar, and batteries have been supplying that rising demand. Utility-scale solar generated 45 terawatt-hours of electricity in the first nine months of 2025. That’s 50% more than the same period in 2024 and nearly four times more than the same period in 2021. Wind generation, meanwhile, totaled 87 terawatt-hours for the first nine months of this year, up 4% from last year and 36% since 2021. “Together,” the analysis stated, “wind and solar generation met 36% of ERCOT’s electricity demand in the first nine months of 2025.”