In a First, UN Climate Talks Address Critical Minerals
Current conditions: Unseasonable warmth of up to 20 degrees Fahrenheit above average is set to spread across the Central United States, with the potential to set records • Scattered snow showers from water off the Great Lakes are expected to dump up to 18 inches on parts of northern New England • As winter dawns, Israel is facing summertime-like temperatures of nearly 90 degrees this week.
THE TOP FIVE
1. Trump opens half of an untouched Alaska reserve to drilling
The Department of the Interior finalized a rule last week opening up roughly half of the largely untouched National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska to oil and gas drilling. The regulatory change overturns a Biden-era measure blocking oil and gas drilling on 11 million acres of the nation’s largest swath of public land, as my predecessor in anchoring this newsletter, Heatmap’s Jeva Lange, wrote in June. The Trump administration vowed to “unleash” energy production in Alaska by opening the 23 million-acre reserve, as well as nearby Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, to exploration. By rescinding the Biden-era restrictions, “we are following the direction set by President Trump to unlock Alaska’s energy potential, create jobs for North Slope communities, and strengthen American energy security,” Secretary of the Interior Doug Burgum said in a statement, according to E&E News. In a post on X, Alaska Governor Mike Dunleavy, a Republican, called the move “yet another step in the right direction for Alaska and American energy dominance.”
The new rule is expected to face challenges in court.“Today’s action is another example of how the Trump administration is trying to take us back in time with its reckless fossil fuels agenda,” Erik Grafe, a lawyer with Earthjustice, an environmental nonprofit group, said in a statement to The New York Times.
2. In a first, UN climate talks address critical minerals
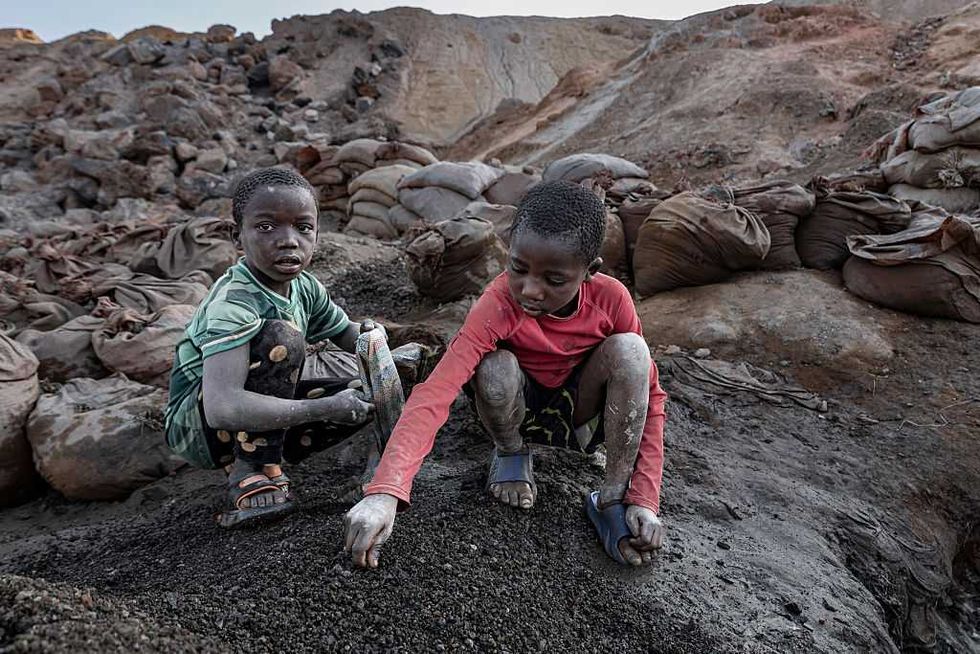

For the first time in United Nations climate negotiations, countries attending the COP30 summit in Belém, Brazil, are grappling with the effects of mining the minerals needed for batteries, solar panels, and wind turbines, Climate Home News reported. In a draft text on Friday, a working group at the summit recognized “the social and environmental risks associated with scaling up supply chains for clean energy technologies, including risks arising from the extraction and processing of critical minerals.”
The statement came amid ongoing protests from Indigenous groups, including those from Argentina who warned that the world’s increased appetite for South America’s lithium reserves came at the cost of local water resources for peoples who have lived in regions near mining operations for millennia.
3. More than 2,600 EPA employees opt for mass resignation
Nearly one fifth of the Environmental Protection Agency’s workforce has opted into President Donald Trump’s mass resignation plan, according to new data E&E News obtained on Friday. The agency had 16,155 employees at the start of this year. As of the end of September, the EPA’s payroll included 15,166 employees, according to data released during the government shutdown, meaning that more than 2,620 employees accepted the “deferred resignation” offer.
Under Administrator Lee Zeldin, the EPA has advanced proposals that even the agency under Scott Pruitt, the top environmental regulator at the start of Trump’s first term, dared not attempt. Zeldin has moved to rescind the endangerment finding, which forms the legal basis for virtually all major climate regulations at the EPA. Zeldin even tried to kill off the popular Energy Star program for efficient appliances, but — as I wrote earlier this month — he backed off the plan.
Sign up to receive Heatmap AM in your inbox every morning:
4. Eavor is preparing to launch its next-generation geothermal technology
The next-generation geothermal company Eavor is preparing to start up its debut closed-loop system at its pilot project in Germany, Think Geoenergy reported. The startup has stood out in the race to commercialize technology that can harness energy from the Earth’s molten core in more places than conventional approaches allow. While rivals such as Fervo Energy, Sage Geosystems, and XGS Energy, pursue projects in the American Southwest, Eavor focused its efforts on Germany, where it saw potential to tap into the lucrative district heating market. Eavor also developed special drilling tools that promised to shave “tens of millions” off the cost of digging wells. As I wrote here last month, the company just completed successful tests of its technology.
5. BlackRock launches a $2.3 billion data center venture with a Spanish firm
BlackRock’s Global Infrastructure Partners inked a deal with the Spanish construction company ACS to form a joint venture to develop roughly $2.3 billion worth of data centers. The 50-50 joint venture will consist of ACS’ existing data-center portfolio, including 1.7 gigawatts of assets under development in Europe, the U.S., and Australia. ACS is contributing its existing portfolio to the business, The Wall Street Journal reported, “in exchange for about 1 billion euros in cash and initial earnout payments of up to 1 billion euros” if the data centers hit certain commercial milestones. “Global demand for data centers is set to grow more than 15 times by 2035, driven by the expansion of AI, cloud migration, and the exponential rise in data volumes,” ACS CEO Juan Santamaria said.THE KICKER
In a first, Swedish scientists have managed to successfully isolate and sequence RNA from an Ice Age wooly mammoth. Researchers at Stockholm University extracted the genetic information from mammoth tissue preserved in Siberian permafrost for nearly 40,000 years. The findings, published in the journal Cell, show that RNA, in addition to DNA and proteins, can be preserved over long periods of time. “With RNA, we can obtain direct evidence of which genes are ‘turned on,’ offering a glimpse into the final moments of life of a mammoth that walked the Earth during the last Ice Age. This is information that cannot be obtained from DNA alone,” Emilio Mármol, lead author of the study, said in a press release.